With Asset allocation strategies at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling scientific with objective tone style filled with unexpected twists and insights.
Asset allocation is a fundamental aspect of investment portfolios, playing a crucial role in managing risk and optimizing returns. In this discussion, we will delve into the various strategies, factors influencing decisions, the importance of diversification, and effective rebalancing techniques.
Importance of Asset Allocation Strategies
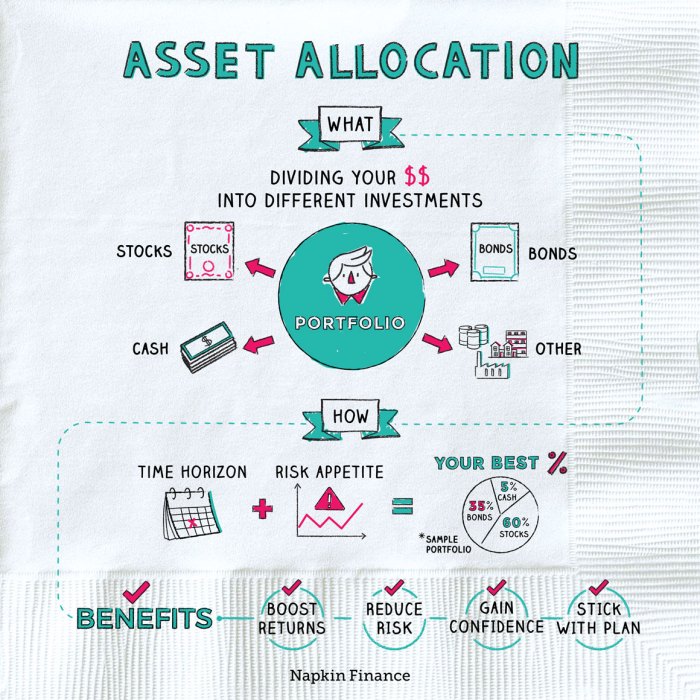
Asset allocation is a critical component of building a successful investment portfolio. By diversifying investments across different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, investors can manage risk and optimize returns.
Managing Risk
Asset allocation helps spread risk across different types of investments, reducing the impact of market fluctuations on the overall portfolio. For example, when one asset class performs poorly, other assets may perform well, balancing out the losses.
Optimizing Returns
By strategically allocating assets based on investment goals and risk tolerance, investors can enhance their chances of achieving higher returns. For instance, a mix of high-risk, high-return investments like stocks with more stable, lower-return investments like bonds can generate a balanced portfolio.
Long-term Financial Goals
Asset allocation plays a crucial role in achieving long-term financial objectives such as retirement planning or wealth accumulation. By adjusting the allocation as goals change and markets evolve, investors can stay on track to meet their financial milestones.
Types of Asset Allocation Strategies
Asset allocation strategies can be broadly categorized into strategic, tactical, and dynamic approaches. Each type of strategy has its own unique characteristics that cater to different risk profiles and investment objectives.
Strategic Asset Allocation
Strategic asset allocation involves setting target allocations for various asset classes and maintaining them over the long term. This approach is based on the investor’s risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals. The key characteristic of strategic asset allocation is its passive nature, as adjustments are only made periodically or in response to significant changes in the investor’s circumstances.
Tactical Asset Allocation
Tactical asset allocation, on the other hand, involves making short-term adjustments to the asset allocation based on market conditions and economic outlook. This approach aims to capitalize on short-term opportunities or mitigate potential risks. Tactical asset allocation requires active management and monitoring of the portfolio to exploit market inefficiencies.
Dynamic Asset Allocation
Dynamic asset allocation combines elements of both strategic and tactical approaches. It involves adjusting the asset allocation based on predefined rules or algorithms that respond to changing market conditions. Dynamic asset allocation seeks to capture upside potential while minimizing downside risk by actively managing the portfolio allocation.
In summary, strategic asset allocation is suitable for investors with a long-term investment horizon and a low tolerance for risk, while tactical asset allocation is more appropriate for investors seeking to capitalize on short-term market opportunities. Dynamic asset allocation offers a balanced approach that adapts to changing market conditions while aiming to achieve optimal risk-adjusted returns.
Factors Influencing Asset Allocation
When determining the appropriate asset allocation strategy, several key factors come into play. These factors play a crucial role in shaping investment decisions and ultimately affect the overall performance of the investment portfolio.
Age, risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial goals are some of the primary factors that influence asset allocation strategies. Let’s delve into each of these factors to understand their impact on investment decisions.
Impact of Age on Asset Allocation
As investors age, their risk tolerance typically decreases. Younger investors may have a higher risk tolerance as they have more time to recover from potential losses. Therefore, younger individuals may opt for a more aggressive asset allocation strategy with a higher allocation to equities. On the other hand, older investors nearing retirement may prefer a more conservative approach with a higher allocation to fixed-income securities to preserve capital.
Effect of Risk Tolerance on Asset Allocation
Risk tolerance refers to an individual’s willingness to withstand fluctuations in the value of their investments. Investors with a higher risk tolerance may choose to allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to equities, which have the potential for higher returns but also come with greater volatility. Conversely, investors with a lower risk tolerance may opt for a more conservative asset allocation with a higher allocation to bonds and cash equivalents.
Influence of Time Horizon on Asset Allocation
The time horizon, or the length of time an investor plans to hold an investment, also plays a significant role in determining the appropriate asset allocation strategy. Longer time horizons allow investors to take on more risk as they have more time to recover from market downturns. Shorter time horizons may necessitate a more conservative approach to protect capital and ensure liquidity when needed.
Impact of Financial Goals on Asset Allocation
Financial goals, such as saving for retirement, funding education expenses, or purchasing a home, can influence asset allocation decisions. Investors with specific financial goals may tailor their asset allocation strategy to achieve those objectives within a certain time frame. For example, someone saving for retirement may choose an asset allocation mix that balances growth potential with capital preservation to meet their long-term financial needs.
Effect of Economic Conditions and Market Trends on Asset Allocation
Economic conditions and market trends can also impact asset allocation choices. During periods of economic uncertainty or market volatility, investors may adjust their asset allocation to reduce risk exposure or capitalize on emerging opportunities. Keeping an eye on economic indicators, market trends, and geopolitical events can help investors make informed decisions when rebalancing their portfolios.
Diversification in Asset Allocation
Diversification is a risk management strategy that involves spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographical regions to reduce overall portfolio risk.
When investors diversify their portfolios, they are essentially spreading their investments across a variety of assets that are not highly correlated with each other. This helps to minimize the impact of any single asset or market sector experiencing a significant decline, as losses in one area can be offset by gains in another.
Benefits of Diversification
Diversifying across asset classes, sectors, and geographies can provide several benefits to investors, including:
- Reduced Portfolio Volatility: Diversification can help smooth out fluctuations in portfolio value by offsetting losses in one asset with gains in another.
- Enhanced Returns: By investing in a variety of assets, investors can potentially capture returns from different market conditions and opportunities, leading to improved overall performance.
- Risk Management: Diversification can help reduce the impact of market volatility and specific risks associated with individual assets or sectors, thus improving the overall risk-adjusted return of the portfolio.
Diversification is often referred to as the only free lunch in investing, as it allows investors to potentially improve risk-adjusted returns without increasing overall portfolio risk.
Rebalancing Strategies
Maintaining the desired asset allocation mix is crucial for investors to achieve their financial goals and manage risk effectively. Rebalancing plays a key role in ensuring that the portfolio stays aligned with the initial investment objectives and risk tolerance of the investor.
Approaches to Rebalancing
There are two main approaches to rebalancing: calendar-based and threshold-based strategies.
- Calendar-based strategy: This approach involves setting specific time intervals, such as quarterly or annually, to review and adjust the portfolio back to its original asset allocation. While this method is systematic and easy to implement, it may not take into account market fluctuations or changes in the investor’s financial situation.
- Threshold-based strategy: In this approach, investors establish predetermined thresholds for each asset class within the portfolio. When the actual allocation deviates beyond these thresholds, rebalancing is triggered to bring the portfolio back in line with the target allocation. This method allows for more flexibility and responsiveness to market movements and changes in the investment landscape.
Benefits of Rebalancing
Rebalancing helps investors stay aligned with their risk tolerance and investment objectives by preventing the portfolio from becoming too heavily weighted in one asset class. It also allows investors to capitalize on market opportunities by buying low and selling high, which can enhance overall portfolio performance over the long term.