Product Pricing Strategies set the stage for profitable business ventures, offering a roadmap to navigate the complex world of pricing dynamics. From cost-plus to value-based strategies, this guide dives deep into the art of pricing for success.
Definition of Product Pricing Strategies
Product pricing strategies refer to the methods and approaches used by companies to determine the price of their products or services. These strategies are essential in achieving business goals, maximizing profits, and gaining a competitive edge in the market.
Examples of Different Product Pricing Strategies
- Penetration Pricing: Setting a low price initially to gain market share quickly.
- Price Skimming: Setting a high price initially and gradually lowering it over time.
- Value-Based Pricing: Setting prices based on the perceived value to the customer.
- Competitive Pricing: Setting prices based on competitor pricing in the market.
The Importance of Having Effective Pricing Strategies in Place
Effective pricing strategies are crucial for businesses to remain competitive, maximize profits, and attract customers. By implementing the right pricing strategy, companies can enhance their brand image, increase customer loyalty, and ultimately achieve long-term success in the market.
Types of Product Pricing Strategies
When it comes to pricing your products, there are several strategies you can consider. Each approach has its own set of advantages and disadvantages that can impact your business in different ways. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common types of product pricing strategies.
Cost-Plus Pricing
Cost-plus pricing involves calculating the total cost of producing a product and then adding a markup to determine the final price. This strategy ensures that you cover all your expenses and generate a profit. However, it may not take into account factors like demand or competition, potentially leading to pricing that is too high or too low.
Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing focuses on the perceived value of a product to customers rather than just the cost of production. By setting prices based on the benefits and value that customers receive, businesses can capture more value from their products. This approach can lead to higher profits but requires a deep understanding of customer preferences.
Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing involves setting a low initial price for a new product to attract customers and gain market share quickly. While this strategy can help businesses enter a competitive market and build a customer base, it may not be sustainable in the long run if prices need to be raised later on.
Competitive Pricing
Competitive pricing involves setting prices based on what competitors are charging for similar products. This strategy can help businesses stay competitive and attract price-conscious customers. However, it may lead to price wars and lower profit margins if not implemented carefully.
Skimming Pricing
Skimming pricing involves setting a high price for a new product to target early adopters and customers willing to pay a premium. Over time, prices are gradually lowered to reach a wider customer base. This strategy can maximize profits from different customer segments but may limit initial sales volume.
Real-World Examples
- Apple uses skimming pricing for its new iPhone releases, attracting early adopters with high prices before lowering them over time to reach a broader market.
- Amazon uses competitive pricing to match or beat prices offered by other retailers, ensuring that customers get the best deal available.
- Tesla employs value-based pricing, setting prices for its electric vehicles based on the innovative technology and environmental benefits they provide.
Factors Influencing Product Pricing: Product Pricing Strategies
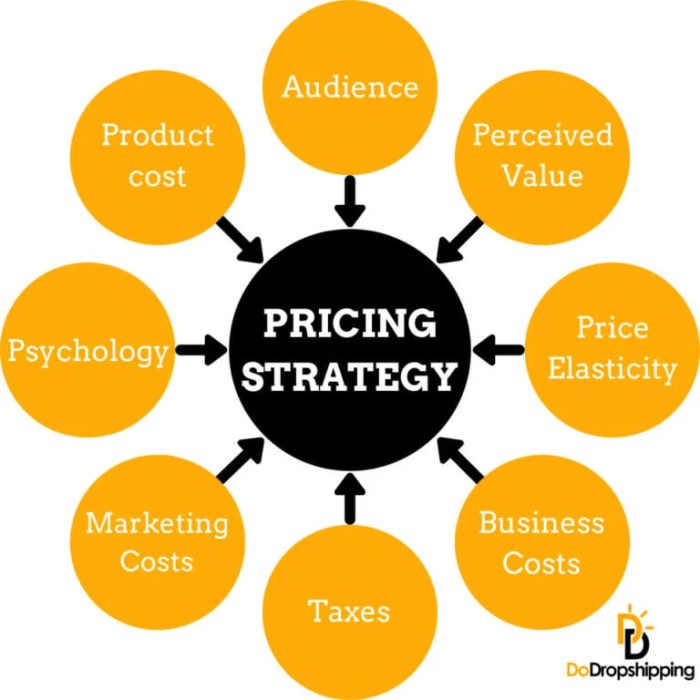
When it comes to setting the price for a product, several key factors come into play. Let’s delve into the main influences that shape product pricing decisions.
Market Demand
Market demand plays a crucial role in determining the price of a product. When the demand for a product is high, a company can afford to set a higher price. On the other hand, if the demand is low, the price may need to be lowered to attract customers.
Competition
Competitor pricing can heavily influence a company’s pricing strategy. In a competitive market, businesses must consider the prices set by their rivals to remain competitive. They may choose to price their products lower, match the competition, or differentiate themselves with higher prices based on value proposition.
Production Costs
The cost of producing a product is a fundamental factor in determining its price. Companies need to cover their production expenses while also making a profit. If production costs increase, it may lead to a higher product price unless companies find ways to optimize costs.
Consumer Behavior
Understanding consumer behavior is essential for setting the right price. Factors like perception of value, willingness to pay, and price sensitivity influence how consumers respond to pricing strategies. Companies need to align their pricing with consumer preferences to maximize sales.
External Factors
External factors such as economic conditions and regulatory environment can also impact pricing decisions. Economic downturns may lead to price adjustments to maintain sales volume, while regulatory changes can affect pricing strategies by imposing restrictions or requirements on pricing practices.
Pricing Strategy Implementation

Implementing a product pricing strategy involves several key steps to ensure the prices set are competitive, profitable, and sustainable in the market. It requires a combination of market research, data analysis, and continuous monitoring to make informed decisions.
Developing a Pricing Strategy
- Conduct Market Research: Understand the market dynamics, customer preferences, competitors’ pricing strategies, and overall industry trends.
- Analyze Costs: Calculate all costs associated with producing, marketing, and distributing the product to determine the minimum price required to cover expenses and generate a profit.
- Set Pricing Objectives: Define the goals of the pricing strategy, whether it’s maximizing profits, gaining market share, or achieving a certain pricing position.
- Choose a Pricing Method: Decide on a pricing method such as cost-plus pricing, value-based pricing, or competitive pricing based on the research and analysis conducted.
Setting and Adjusting Prices, Product Pricing Strategies
- Initial Price Setting: Determine the initial price based on the pricing strategy developed, taking into account costs, competition, and customer value perception.
- Monitor Competitors: Keep track of competitors’ pricing changes and market reactions to adjust prices accordingly to stay competitive.
- Price Testing: Conduct price testing to evaluate customer response to different price points and make adjustments based on the results.
- Dynamic Pricing: Implement dynamic pricing strategies to respond to changes in demand, seasonality, or other market factors.
Data Analysis and Monitoring
- Utilize Data Analytics: Use data analytics tools to analyze sales data, customer behavior, and pricing impact on revenue to make data-driven pricing decisions.
- Customer Feedback: Gather feedback from customers on pricing perceptions, value proposition, and willingness to pay to make necessary adjustments.
- Regular Review: Continuously review pricing strategies, performance metrics, and market conditions to identify opportunities for improvement and optimization.
- A/B Testing: Conduct A/B testing on pricing strategies, promotions, and discounts to determine the most effective pricing tactics for different customer segments.